Appraising the Impact of Digital Transformation on Indian Financial Services Industry
Abstract:
This research aims to assess the impact of digital transformation on the Indian financial services industry. The rapid advancement of digital technologies has revolutionised various aspects of financial services, including banking, payments, lending, insurance, and wealth management. This study explores the key drivers of digital transformation in the Indian context, identifies the challenges and opportunities associated with this transformation, and evaluates its effects on industry stakeholders, consumers, and the overall financial ecosystem. The research employs quantitative analysis of industry data to gain a comprehensive understanding of the topic. The findings will contribute to the existing literature on digital transformation in the financial sector and provide insights for policymakers, industry players, and consumers to navigate the evolving landscape.
Introduction:
Digital transformation has become a pervasive force in shaping various industries worldwide, and the financial services sector is no exception. In India, where technological advancements have gained significant traction in recent years, the influence of digital transformation on the financial services industry is rapidly unfolding. This transformation is fundamentally altering the way financial services are delivered, accessed, and experienced by consumers and businesses alike.
The Indian financial services sector, encompassing banking, insurance, lending, payments, and wealth management, is undergoing a paradigm shift driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. The adoption of digital technologies and innovative solutions has the potential to revolutionise traditional business models, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, and drive financial inclusion in a country with a vast unbanked population.
One of the key driving forces behind digital transformation in the Indian financial services sector is the rapid proliferation of technology. The rise of mobile devices, advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and the internet of things (IoT) have paved the way for new opportunities and innovative business models. These technologies enable financial institutions to provide seamless and personalised services, facilitate faster and more secure transactions, and gain deeper insights into customer behaviour and preferences.
Moreover, changing consumer expectations and behaviours are shaping the landscape of financial services in India. The rise of the digitally native millennial generation, along with a growing tech-savvy middle class, has created a demand for convenient, user-friendly, and digitally-enabled financial solutions.
Consumers now expect 24/7 accessibility, personalised experiences, and seamless integration across multiple touchpoints, leading financial service providers to reimagine their offerings and delivery channels.
The Indian government's focus on promoting a digital economy and financial inclusion has further accelerated the digital transformation in the financial services sector. Initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) and Unified Payments Interface (UPI) have facilitated greater financial access and encouraged digital payments. These efforts have not only transformed the way people transact but also opened doors for new players and disruptive technologies in the sector.
However, as digital transformation gains momentum, it also brings forth challenges and considerations that need to be carefully addressed. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures, safeguarding customer data privacy, navigating complex regulatory frameworks, and bridging the digital divide across different sections of society are some of the critical aspects that require attention.
In this study, the author aims to assess the influence of digital transformation on the Indian financial services sector, examining its implications for stakeholders, analyzing the challenges and opportunities, and exploring the transformative potential of digital technologies. By employing a comprehensive research approach, the author intends to provide valuable insights and actionable recommendations for industry players, policymakers, and consumers to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape.
Research Methodology:
To assess the influence of digital transformation on the Indian financial services sector, the author has employed a ‘quantitative analysis’ approach.
Quantitative analysis involves collecting and analyzing relevant industry data, financial reports, market trends, and performance indicators. This data is used to identify key trends, patterns, and quantitative measures of the impact of digital transformation on the sector. Statistical techniques such as regression analysis and data visualisation will be utilised to derive meaningful insights from the quantitative data.
Quantitative research will allow for a holistic understanding of the influence of digital transformation on the sector. It will provide a comprehensive view of the aspects related to stakeholder experiences, challenges, and opportunities. The findings will be synthesised to draw meaningful conclusions and provide actionable recommendations for policymakers, industry participants, and consumers navigating the digital transformation of the Indian Financial Services Industry.
Literature Review:
The Indian Financial Services Industry is in the midst of a digital revolution that is reshaping how we manage money. It is not just about fancy apps; it is a seismic shift in how banks, insurers, and even startups operate.
In the ever-evolving financial industry, customer-centric transformation is at the forefront of strategic initiatives. Fintech disruption has forced traditional institutions to prioritise data-driven decisions, harnessing the power of data analytics and AI adoption to stay competitive. Simultaneously, the regulatory landscape is undergoing significant evolution, presenting both challenges and opportunities for financial organisations. As they navigate these changes, achieving financial inclusion remains a vital goal. Understanding shifting consumer behaviours is key in this endeavour. Moreover, cost efficiency and operational excellence are essential to adapt to the changing market dynamics, ensuring sustainable growth in this dynamic and complex environment.
Amidst the ongoing financial transformation, one of the paramount challenges faced by the industry is the escalating cybersecurity concerns. As financial organisations embrace digitalization and data-driven strategies, they become increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. Safeguarding sensitive customer data and ensuring the integrity of financial transactions are imperative in this environment. The evolving regulatory landscape also places stringent demands on cybersecurity measures, making it essential for businesses to continuously invest in robust cybersecurity solutions and stay ahead of cyber threats to maintain trust and security in the financial sector.
In summary, the digital transformation of the Indian Financial Services Industry has reshaped the sector in various ways, including improving financial inclusion, fostering fintech innovation, enhancing data-driven decision-making, and necessitating regulatory adaptation. Understanding these impacts is essential for comprehending the ongoing transformation of this vital industry. Further research and case studies are needed to monitor and analyse the evolving landscape of digital transformation in the Indian Financial Services Industry.
Objectives:
This study aims to study the following objectives:
1. To assess the impact of digital transformation:
Evaluate how digitalization is changing customer experiences, operational efficiency, and financial services accessibility in India.
2. To identify key drivers:
Uncover the primary factors driving digital transformation within the financial industry.
3. To analyse challenges:
Examine challenges such as cybersecurity, regulatory adaptation, and legacy systems hindering the transformation process.
4. To evaluate future prospects:
Explore the potential long-term effects of digitalization on the Indian financial landscape.
5. To analyse regulatory implications: Examine how regulatory changes adapt to the digital shift, balancing innovation and stability.
6. To inform strategic decision-making: To provide insights that assist industry stakeholders in making informed decisions regarding digital strategies and investments.
7. To assess the effects of digital transformation:
Evaluate how digitalization is reshaping services, customer experiences, and business models in Indian finance.
8. To explore inclusion impact: Investigate how digital finance initiatives impact financial inclusion and accessibility in India.
Analysis/ Inference:
The following figure depicts the digitalisation in the Indian Financial System. On the X axis, we have, “years” starting from 1980 till 2020 and on the Y axis, we have, “impact of digitalisation”. Now, digitalisation being a non-quantifiable unit, the author has made use of arbitrary units to quantify a non-quantifiable unit metric, i.e., a variety of units like - increase in the customer base, different operations introduced in the financial sector, etc.
In the year 1980, one may observe almost no impact of digitalisation. But in 1990, a decade later, we can see a sharp increase, illustrating a rise in both; digitalisation and the impact on the Indian Financial Sector. In the upcoming years, i.e., in the year 2000 and 2010, we see a further rise. Talking about 2020, there is an extremely rapid surge. This is an indicator of the various digital projects undertaken in an economy. That is not all. The upward sloping curve from left to right shows us that by the next decade, we can only imagine the digital revolution that would take place in the Indian economy. Hence, the future is very promising.
Introducing Statistical Measures (Regression Analysis):
Regression analysis describes the relationships between a set of independent variables and the dependent variable. Regression analysis produces a regression equation where the coefficients represent the relationship between each independent variable and the dependent variable.
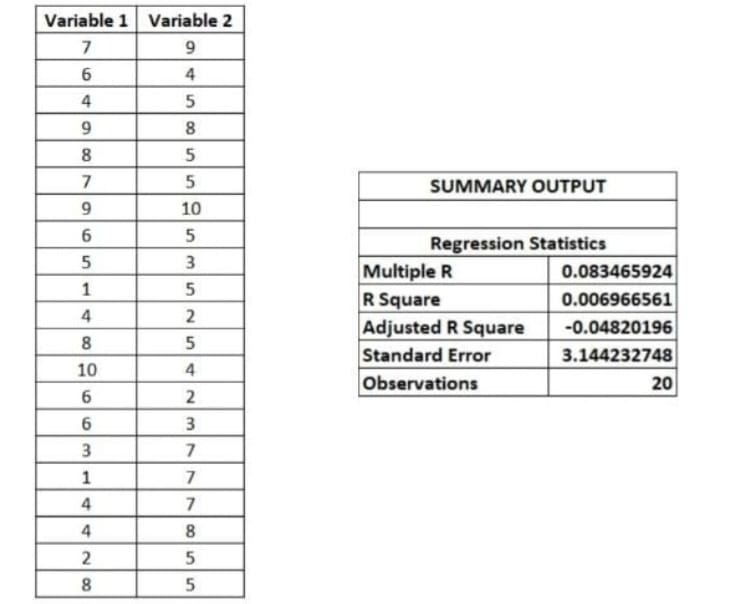
Here, we have two variables - “Variable 1” and ”Variable 2”. Variable 1 studies the increase in digitising the economy. Variable 2 is the effect of the digitalisation. So this regression model is the extent-effect ridden. Also, the level of significance is 95%. The “Summary Output” gives a detailed report of the regression analysis performed.
The above table shows the value of p (or p-value), viz., 0.001263. Since the p-value is less than 0.5, we can conclude that the independent variable is affected by the dependent variable.1
1. A low P-value (< 0.05) means that the coefficient is likely not to equal zero. A high P-value (> 0.05) means that we cannot conclude that the explanatory variable affects the dependent variable.
Findings and Observations:
In the realm of digital transformation within the Indian Financial Services Industry, several notable trends and observations have come to light:
1. Fintech Disruption: Fintech firms have disrupted traditional banking, offering user-friendly services, forcing traditional players to innovate.
2. Data's Power: Data-driven decision-making is key, with AI and analytics driving personalised services and risk management.
3. Regulatory Evolution: Regulators are adapting, striking a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding financial stability.
4. Financial Inclusion: Digitalization has made financial services accessible to previously underserved populations, promoting financial inclusion.
5. Challenges Persist: Legacy systems, cybersecurity threats, and the need for digital literacy remain significant challenges in this transformative journey.
Recommendations:
Based on the appraisal of digital transformation's impact on the Indian Financial Services Industry, several key recommendations emerge:
1. Invest in cybersecurity:
Given the growing threat landscape, financial institutions must prioritise robust cybersecurity measures to protect customer data and systems.
2. Continued regulatory adaptation: Regulators should maintain a proactive stance, keeping pace with technological advancements while safeguarding consumer interests.
3. Foster innovation:
Encourage collaboration between traditional financial institutions and fintech firms to foster innovation, delivering customer-centric solutions.
4. Digital literacy programs:
Promote digital literacy initiatives to bridge the gap and ensure that all segments of society can benefit from digital financial services.
5. Data ethics:
Establish clear data ethics guidelines to balance data-driven innovation with customer privacy and security.
6. Long-term strategy:
Financial organisations should adopt a long-term digital transformation strategy, recognizing that this shift is an ongoing process rather than a one-time event.
By implementing these recommendations, India's financial sector can navigate the digital transformation landscape effectively, ensuring it remains inclusive, secure, and resilient to future disruptions.
Conclusion:
Digital transformation is undeniably reshaping the Indian Financial Services Industry. Fintech innovations have disrupted traditional banking, ushering in an era of customer-centricity and accessibility. Data-driven decision-making, though powerful, necessitates stringent cybersecurity measures and data ethics considerations.
Regulators play a pivotal role in maintaining a balance between innovation and stability. Financial inclusion has expanded, yet challenges like legacy systems and digital literacy persist.
In conclusion, India's financial landscape is evolving rapidly, offering immense opportunities for those who embrace digital transformation while highlighting the critical need for strategic planning, collaboration, and a commitment to security and inclusion. The industry's future success hinges on its adaptability and responsiveness to this digital revolution.
Refrences:
I. Research Papers
1. “Digitalization and the future of work in the financial services sector” - Issues paper for the Technical meeting on the impact of digitalization in the finance sector (Geneva, January 24th – 28th, 2022)
https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---sector/documents/meetingdocument/wcms_824708.pdf
2. “Digital Transformation Shaping the Future of The Finance Industry” - IBEF (April 2023)
https://www.ibef.org/research/case-study/digital-transformation-shaping-the-future-of-the-finance-industry
II. Newspaper Articles
1. “Digital Transformation in the Financial Sector” by The Times Of India. (Published - September 15th, 2022)
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/voices/digital-transformation-in-the-indian-financial-sector/
2. “Digital Transformation: Creating flux in the financial sector” by Forbes India. (Published - October 27th, 2017)
https://www.forbesindia.com/article/forbes-india-leaderspeak/digital-transformation-creating-flux-in-the-financial-sector/48517/1
III. Statistical and Graphical Representation
1. Calculating and displaying regression statistics in excel
https://www.rwu.edu/sites/default/files/downloads/fcas/mns/calculating_and_displaying_regression_statistics_in_excel.pdf
Researched By-
Aanuj Shrotriya



Comments
Post a Comment